Laws
1.Wien's law
Wien's (displacement) Law relates the temperature of an object to the maximum wavelength at which it radiates energy, since as the temperature of an object increases the maximum wavelength will decrease. In this way, stars of different temperatures appear as different colours in the electromagnetic spectrum, with hotter stars appearing bluer and cooler stars appearing redder.
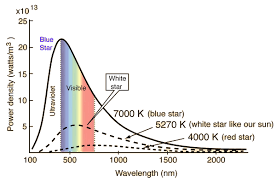
T=(2.9·106k·m)/λmax
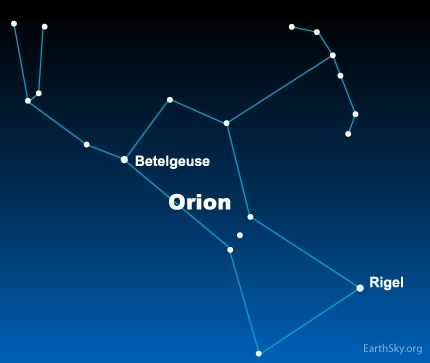
Rigel (blue) λmax = 240 m → T ≈ 12000 K
Beteleguese (red) λmax = 830 m → T ≈ 3500 K
Sun λmax ≈ 500 m → T? T = 5800K
2.Stefan-Boltzmann's law
Stefan-Boltzmann's law relates the luminosity of a star to its surface area and temperature. It states that the luminosity of a star is a function of both its radius and its surface temperature.
